Eosinophilic esophagitis – Warning signs and management

Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic immune system disease that causes a type of white blood cells, eosinophils, to build up along the lining of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. When affected by the buildup of white blood cells, it can become inflamed or injured, leading to issues with food intake. Here, recognizing the following signs can help seek treatment for the condition.
Signs
Here are a few common symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) that can make it easy to get an early diagnosis and treatment for the condition:
1. Dysphagia
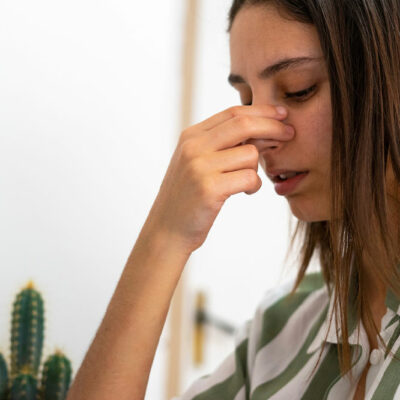
Dysphagia is one of the most common signs of eosinophilic esophagitis. It refers to difficulty swallowing food or drinks. Here, the lining of the food pipe or esophagus can become swollen, making it difficult and sometimes painful to swallow foods and beverages. To deal with this sign, one may have to opt for smaller bites of food that are easier to swallow and less likely to result in choking. Further, one should take one small bite at a time instead of a mouthful. Chewing slowly also helps lower the risk of choking. Additionally, taking small sips of water or other beverages in between bites can help push the food down with ease. Another important change to make here is the posture while eating or drinking. Sitting up straight and avoiding slouching or lounging can ease the process of eating and drinking when dealing with dysphagia.
2. Food impaction
This is another symptom brought on by the inflammation in the food pipe. The swelling, along with the progressive fibrosis and the narrowing of the esophageal lumen, can make the food get stuck in the esophagus after it is swallowed. This is known as impaction. The severity of the symptom varies from person to person, however, if the condition remains untreated or unmanaged, it can worsen. Impaction requires immediate attention from a health professional, as food stuck in the esophagus can lead to choking. Endoscopic intervention may be required to deal with the issue. So, one should keep an eye out for this sign and, upon noticing it, seek timely intervention to prevent further complications.
3. Chest pain
If the food pipe is inflamed, swallowing foods and drinks can further irritate the lining of the wall, leading to chest pains. Such aches cannot be managed with acidity treatment. So, if one notices centrally located chest pain that does not respond to acidity prescription treatment, they should consider getting tested for eosinophilic esophagitis.
4. Regurgitation
Also associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD, regurgitation may have links with low-level eosinophilia. Both conditions can lead to a backward flow of undigested food, known as regurgitation. In particular, the difficulty swallowing food and food impaction can lead to vomiting when dealing with eosinophilic esophagitis.
Symptoms in children
The symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis, although similar to those observed in adults, require special attention. This is because children may not be able to voice the discomfort associated with the condition. Some of the warning signs to recognize are:
- Any vomiting after a meal
- Difficulty eating altogether
- Difficulty feeding infants
- Abdominal pain that children may mention
- Difficulty swallowing foods and drinks
- Food stuck in the esophagus often and frequently
- Symptoms of GERD and no response to GERD treatment
Other warning signs to recognize are any signs of malnutrition, delayed physical growth, and extended inactivity. Keeping an eye out for such health issues can help one seek timely treatment for the affected child and prevent further complications.
Management options
First, a detailed diagnosis can help in understanding the exact cause and severity of the symptoms when dealing with EoE. Following this, a customized treatment plan can help in relieving the symptoms and preventing EoE flare-ups. Here are the common components of an eosinophilic esophagitis treatment plan:
Nutritional changes: Here, by following an elimination food regimen, one may be able to recognize foods that trigger a flareup. Further, food allergy and nutritional deficiency tests can help doctors determine the nutritional changes to make. Based on the results, one may have to add or avoid certain foods and drinks when managing EoE. Often, cutting down on dairy and wheat products can help reduce inflammation. Other food-based limitations can be recommended by a nutritionist depending on individual nutritional requirements and sensitivity to certain ingredients.
Dilation: This is a procedure involving stretching of the esophagus if it has become too narrow. Dilation can help ease swallowing without the use of prescription treatment. However, following the procedure, one may experience chest pains that can last for a couple of hours or even days.
In addition to undergoing prescribed treatment, certain home remedies and lifestyle changes can help in managing the condition. Recognizing triggers and avoiding them is a crucial part of managing eosinophilic esophagitis. Common triggers here include spicy food, mint, garlic, chocolate, fried foods, tomato sauce, caffeine, and onion. These foods can trigger heartburn. So, one should limit or avoid known triggers, apart from making nutritional changes recommended by a doctor. Further, leading an active lifestyle by exercising regularly can help improve overall health.