Thyroid eye disease – Symptoms, causes, and management

Thyroid eye disease, also popularly known as Grave’s disease, is an autoimmune condition in which specific eye muscles and tissues become inflamed. An autoimmune response causes inflammation, as the body attacks its own tissues when it perceives a threat. Grave’s or thyroid eye disease is categorized by swelling around the eyelids, bulged eyes, blurry vision, and vision impairment of varying degrees if not managed on time. Here are a few things to know about this condition:
Symptoms
There are a few common signs that help professionals diagnose thyroid eye disease. These are as follows:
- Changes in the eyes
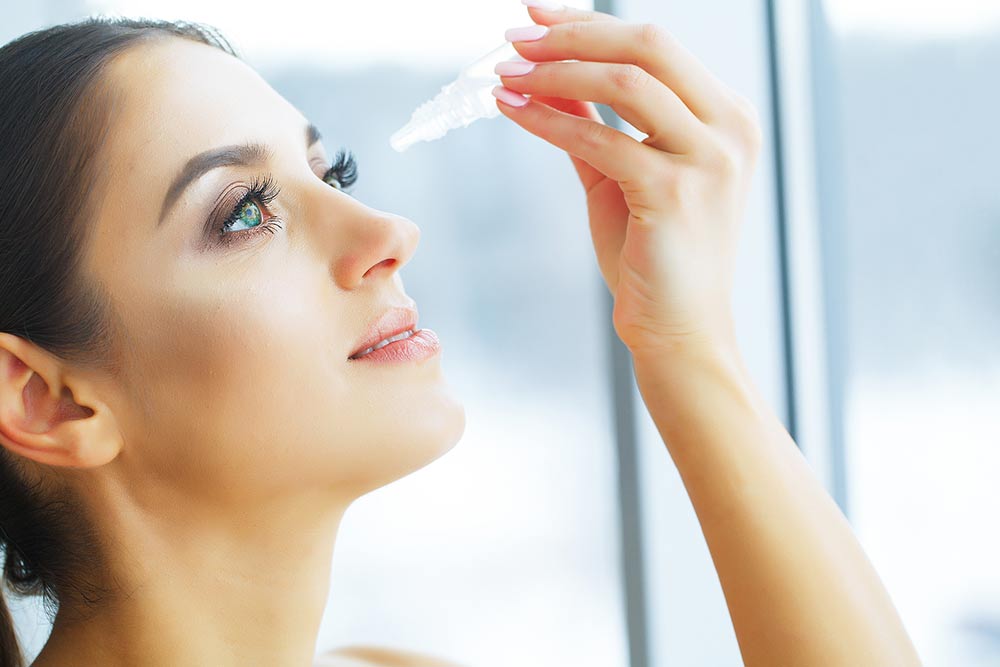
The condition is characterized by the swelling of the tissues and muscles in and around the eyes. As a result, patients may experience swelling around the eyelids, bloodshot eyes, and undereye bags. Additionally, all these symptoms make the eyes appear disproportionately huge and bulgy. The pupils also appear smaller in comparison to the rest of the eyes. - Low tolerance of bright lights
The inflammation and swelling of one’s eye muscles also cause muscle weakness. As a result, all the various parts of a person’s eyes, such as the cornea and iris, become more strained when an individual with this condition stares at bright lights. - Blurry vision
Mismanagement or an untimely diagnosis can also lead to vision impairment in those with this condition. Some early symptoms to look for include blurry vision and, in many cases, the inability to differentiate between things clearly beyond a certain range. This happens as the light does not get adequately transmitted and electrical impulses do not reach the brain properly due to nerve damage in the eyes. - Watery eyes
It is common for people with thyroid eye disease to have watery eyes due to the swelling and inflammation in the optic region, such as the tear ducts. This causes watery eyes and irritation around the eyes.
Causes
While there are usually no known causes for most autoimmune diseases, certain risk factors can increase one’s chances of being diagnosed with Grave’s disease. Autoimmune conditions occur when a person’s immune system goes into overdrive and mistakenly attacks its own tissues when it perceives certain internal and external threats. The body increases its white blood cell production. Excess white blood cells in the body are a marker of inflammation.
Usually, people with this autoimmune condition may also develop other autoimmune disorders in the future. Apart from over-aggressive immune activity, thyroid eye disease can also be triggered by the over-activity or under-performance of a person’s thyroid gland.
Management
While autoimmune conditions like Grave’s disease are not curable and are often lifelong, making certain lifestyle changes and following a doctor’s treatment plan can put them into remission. Grave’s disease is manageable, and one can follow a few management methods. That said, making these changes slowly and under one’s doctor’s supervision is recommended.
- Lifestyle changes and natural remedies
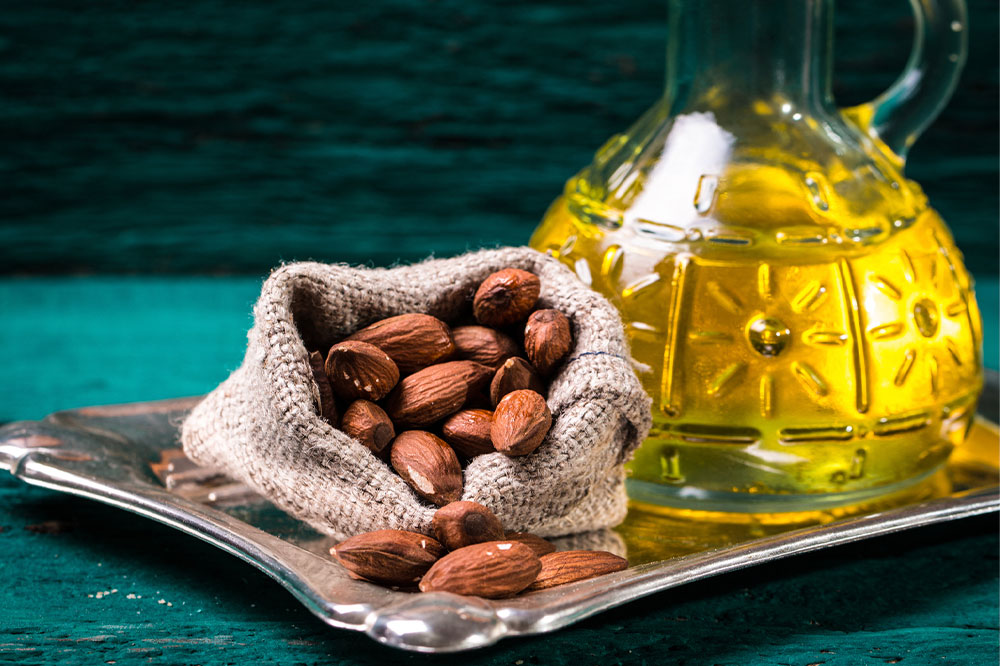
Some of the best ways to manage thyroid eye disease involve making specific changes to one’s lifestyle and using some home remedies. Patients with Grave’s disease can consider applying warm and cool compresses to their eyes when they notice signs of swelling. This helps inhibit the inflammation to a certain degree. They should also wear sunglasses to reduce sun exposure and strain. Those with thyroid eye disease should also consider sleeping with their head slightly elevated. Additionally, applying tape to the eyelids before sleeping can help, as those with this condition can often not close their eyes due to inflammation. The inability to shut one’s eyes for a prolonged period can cause corneal cancer, a condition in which loss of vision and eye scars occur. Other remedies include wearing an eye patch on one eye to offset the double vision caused by thyroid eye disease. Double vision can also be neutralized by wearing glasses with prisms.Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as nuts, fatty fish, and olive oil, is one lifestyle change people can adopt, as omega-3 fatty acids help decrease inflammation. Most importantly, one must keep their thyroid levels in check by following their healthcare provider’s suggestions and testing themselves regularly for any irregularities. Some of the best foods for preventing or reducing the severity of thyroid eye disease include fruits and vegetables, legumes, whole grains, fish, nuts, and seeds. Green leafy vegetables like spinach and broccoli are also effective in reducing inflammation in the eyes and other areas of a person’s body. The fiber in these vegetables and legumes is great for reducing inflammation. - Orbital decompression surgery
It helps relieve pressure on one’s optic nerve and reduces inflammation to a great extent. This is one of the treatment methods with a high success ratio. Apart from this, eyelid and muscle surgeries are also two other options to consider. If they notice any issues post-surgery, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended.